- Air infiltration: Limit air leakage through fixed glazing and frames to 0.026 cfm/ft2/min (0.01 L/s/m2) when tested in accordance with ASTM E-283-04 at a cross pressure of 6.24 psf (0.30 kPa).
- Water Penetration under Static Pressure: System shall not evidence uncontrolled water penetration at a cross pressure of 15 psf (103 kPa) when tested in accordance with ASTM-E331-00.
- Water Penetration under Dynamic Pressure: System shall not evidence uncontrolled water penetration at a cross pressure of 15 psf (103 kPa) when tested in accordance with AAMA-501.1-05.
1.1 REFERENCES
A. American Architectural Manufacturers Association (AAMA):
-
1. AAMA/NWWDA 101/I.S. 2-97 - Voluntary Specification, Performance Requirements and Test Procedures for Air Leakage Resistance, Water Penetration Resistance, Structural Loading, Forced Entry Resistance.
2. AAMA-501.1 - Standard Test Method for Water Penetration of Windows, Curtain Walls and Doors Using Dynamic Pressure.
3. AAMA 501.4 - Recommended Static Test Method for Evaluating Curtain Wall and Storefront Systems Subjected to Seismic and Wind Induced Interstory Drifts.
4. AAMA 2605 - Voluntary Specification, Performance Requirements and Test Procedures for Superior Performing Organic Coatings on Aluminum Extrusions and Panels.
B. ASTM International (ASTM):
-
1. ASTM B 221 - Standard Specification for Aluminum and Aluminum-Alloy Extruded Bars, Rods, Wire, Profiles, and Tubes.
2. ASTM E 283 - Test Method for Determining the Rate of Air Leakage Through Exterior Windows, Curtain Walls, and Doors under Specified Pressure Differences across the Specimen.
3. ASTM E330 - Standard Test Method for Structural Performance of Exterior Windows, Doors, Skylights and Curtain Walls by Uniform Static Air Pressure Difference.
4. ASTM E 331 - Test Method for Water Penetration of Exterior Windows, Curtain Walls, and Doors by Uniform Static Air Pressure Difference.
5. ASTM E 1886 - Standard Test Method for Performance of Exterior Windows, Curtain Walls, Doors, and Impact Protective Systems Impacted by Missile(s) and Exposed to Cyclic Pressure Differentials.
6. ASTM E 1996 - Standard Specification for Performance of Exterior Windows, Curtain Walls, Doors and Impact Protective Systems Impacted by Windborne Debris in Hurricanes.
C. National Fenestration Rating Council (NFRC):
-
1. NFRC-100 - Procedure for Determining Fenestration Product U-factors.
2. NFRC-200 - Procedure for Determining Fenestration Product Solar Heat Gain Coefficient and Visible Transmittance at Normal Incidence.
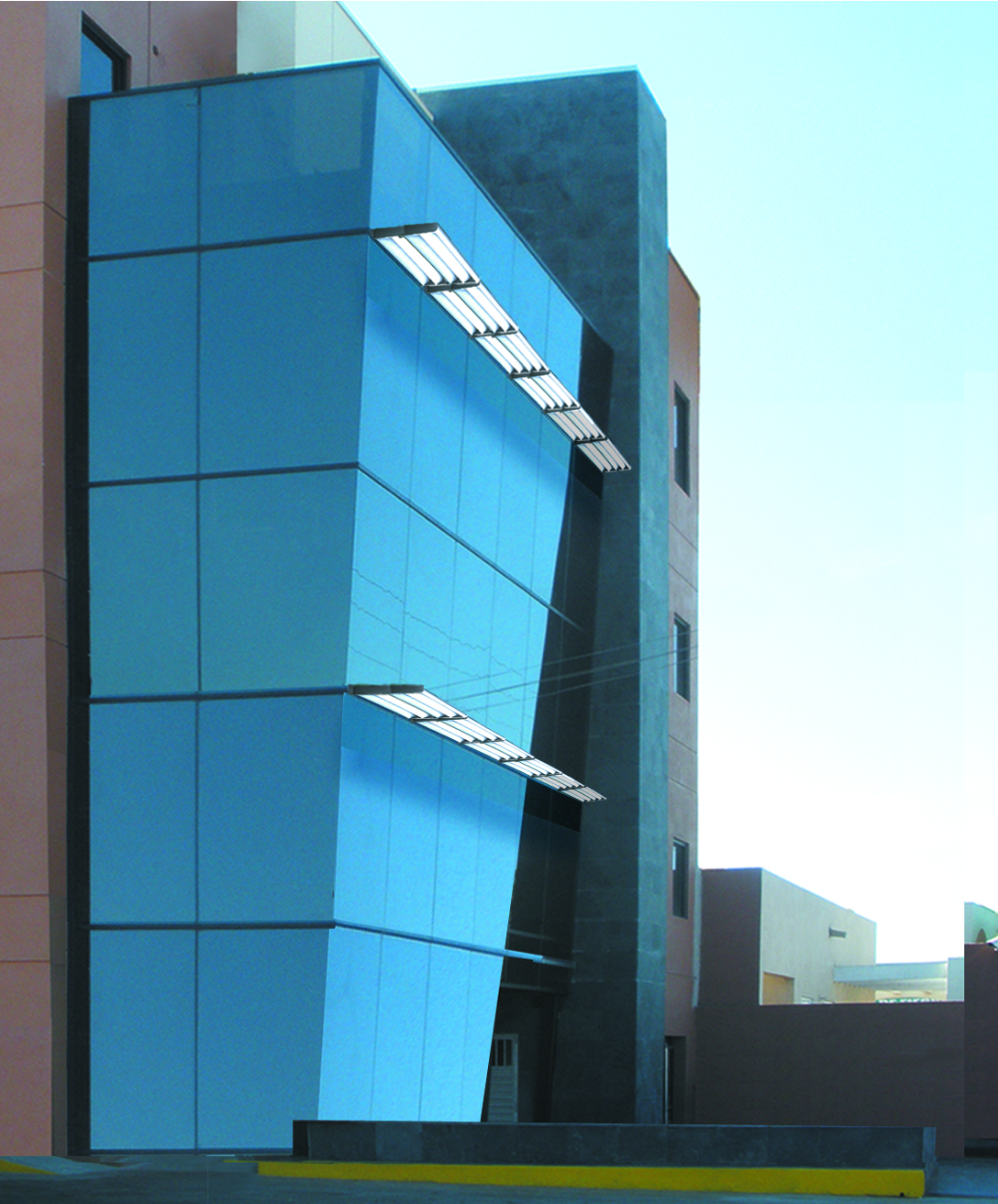
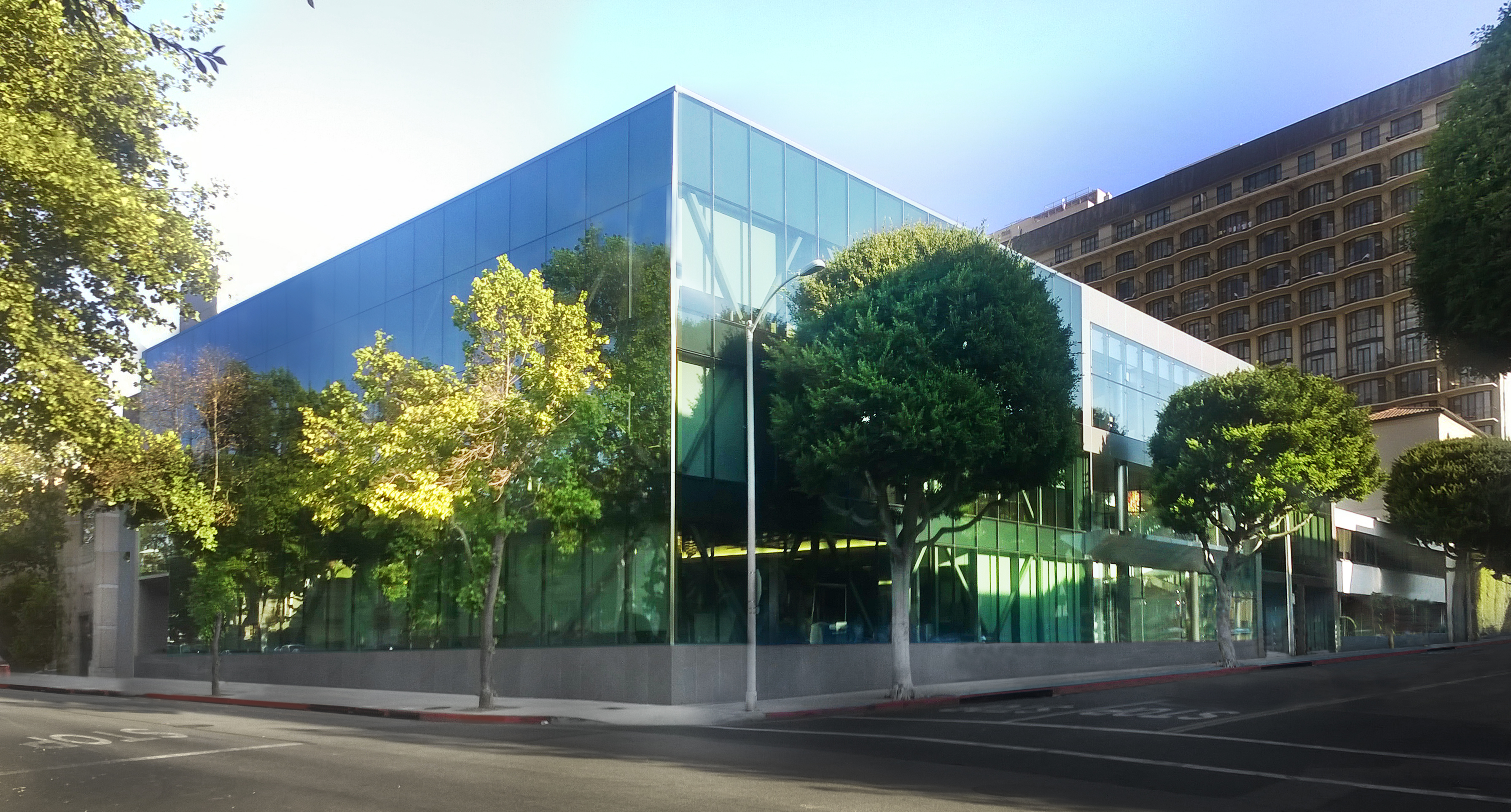
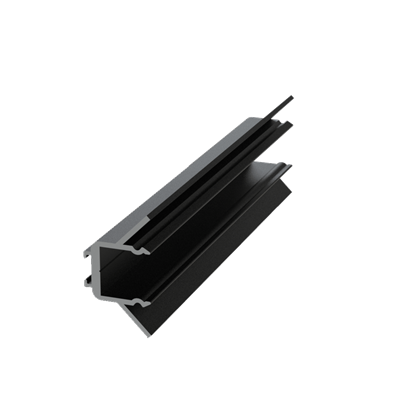
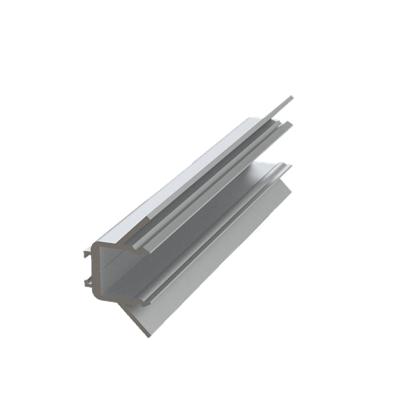
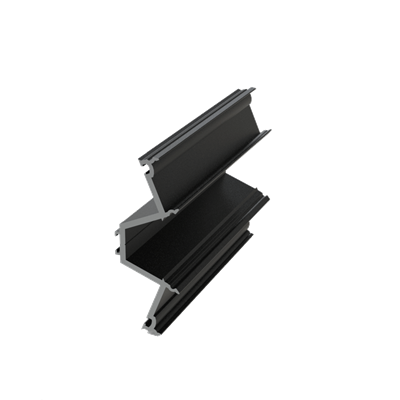
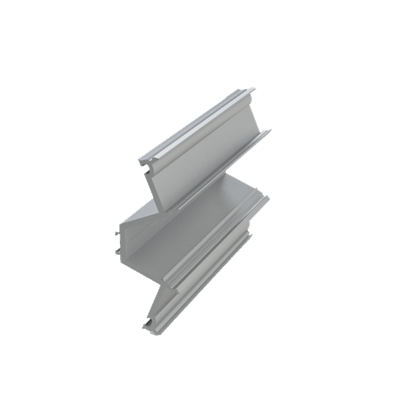
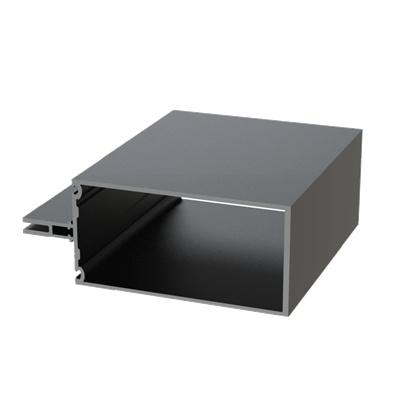
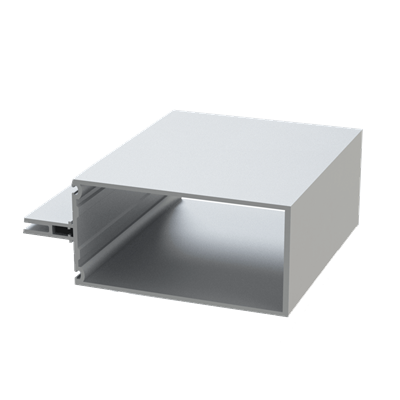
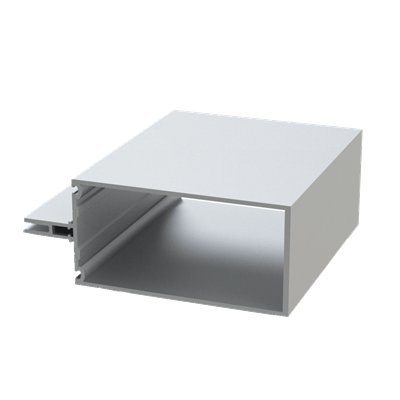
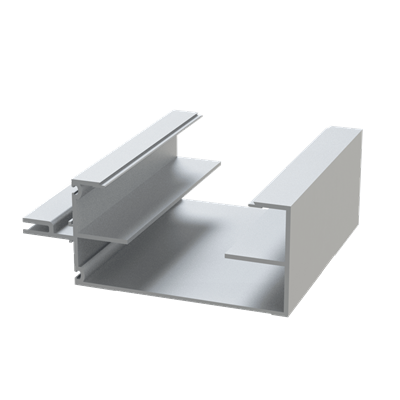
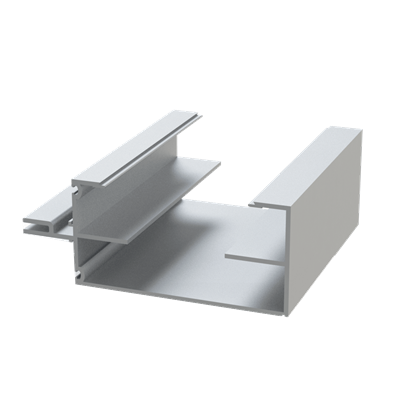
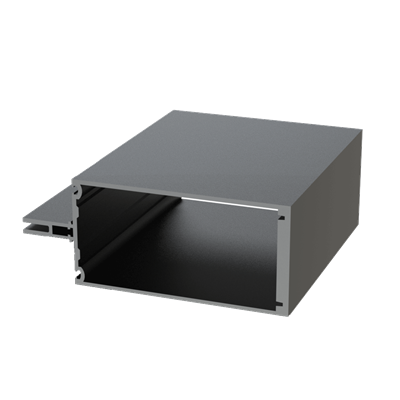
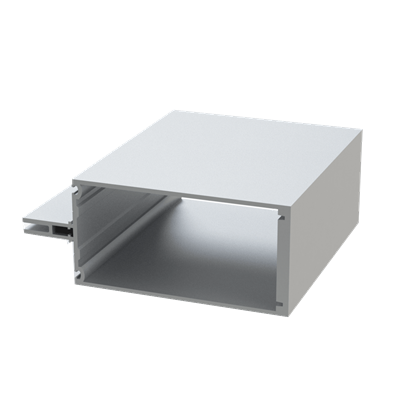
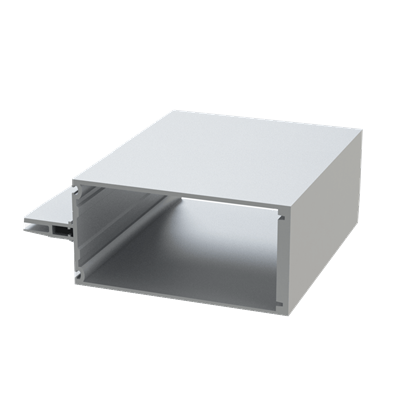
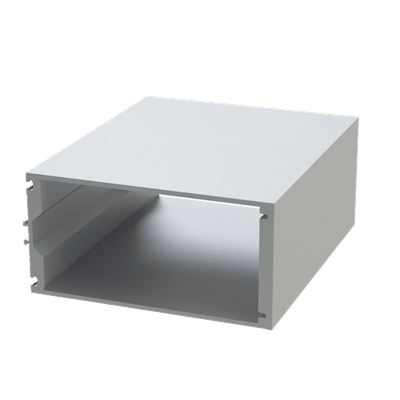
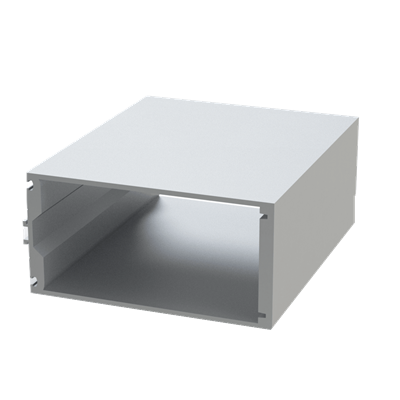
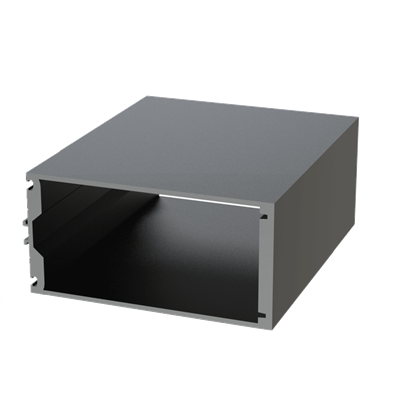
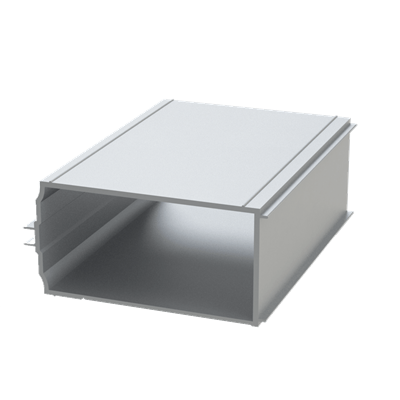
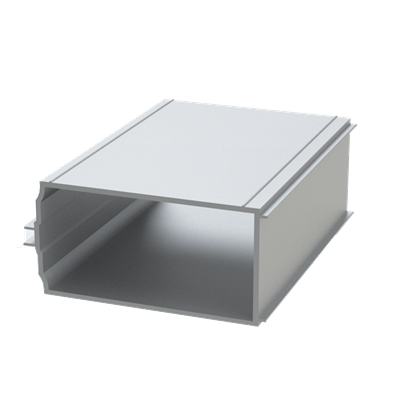
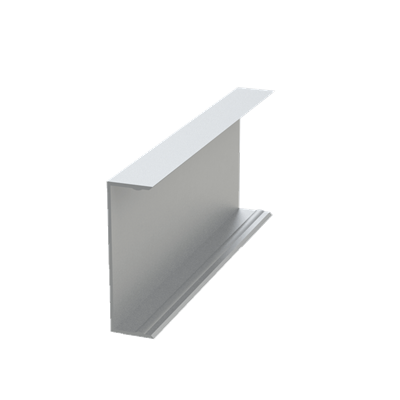
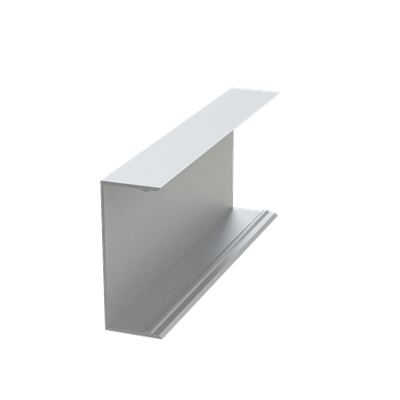
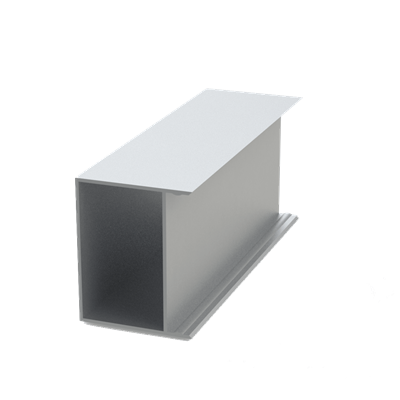
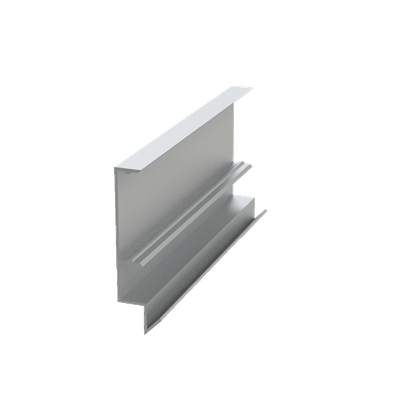
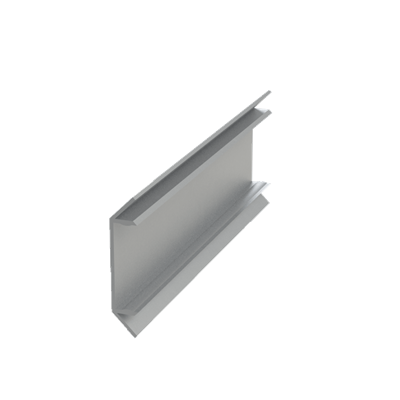
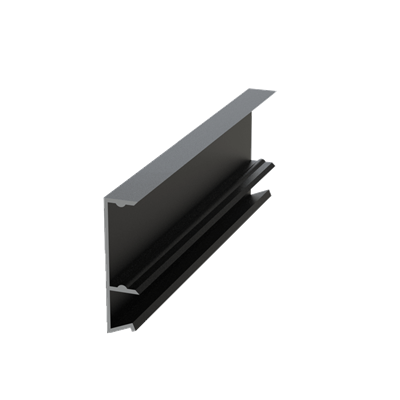
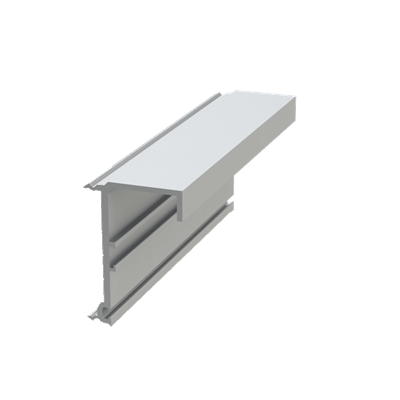
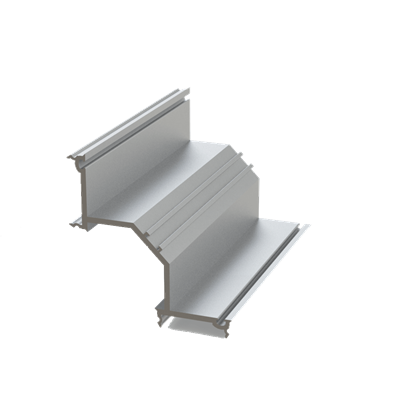
These installation instructions are generic in nature but specific to the PRL curtain wall systems. They are specific to all of PRL’s curtainwalls including the PLCW-600, PLCW-700 and PLCW-1000. Because each project will have differing conditions, each project should have job specific drawings prepared by journeymen drafters or engineers who are familiar with curtain-wall construction and have an intimate understanding of PRL’s curtain wall system and how to integrate it into the construction details specific to the project it is being used on. The shop drawings will take precedence over these instructions as they are project specific. You may refer to PRL’s test reports for further familiarity with construction details of the curtain walls. When in doubt contact your PRL technical representative.
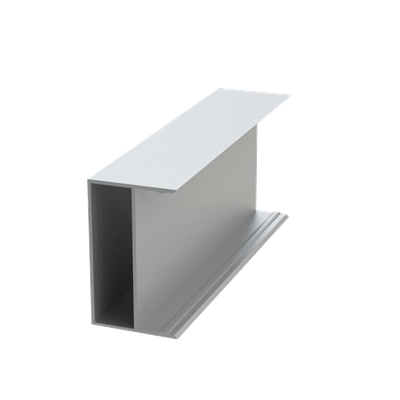
PROJECT NAME = cw701 PROJECT NUMBER=1
Ixx - NEUTRAL MOMENT OF INERTIA = 7.77083 AREA = 1.84775
Iyy - NEUTRAL MOMENT OF INERTIA = 1.71654 PERIMETER = 19.7867
Ixy - NEUTRAL MOMENT OF INERTIA = .000000
Ip - POLAR MOMENT OF INERTIA = 9.48737
Imax - MAXIMUM MOMENT OF INERTIA = 7.77083
Imin - MINIMUM MOMENT OF INERTIA = 1.71654
Theta - PRINCIPLE TO LOCAL ANGLE = .000000
Rmax - MAXIMUM RADIUS OF GYRATION= 2.05074
Rmin - MINIMUM RADIUS OF GYRATION= .963840